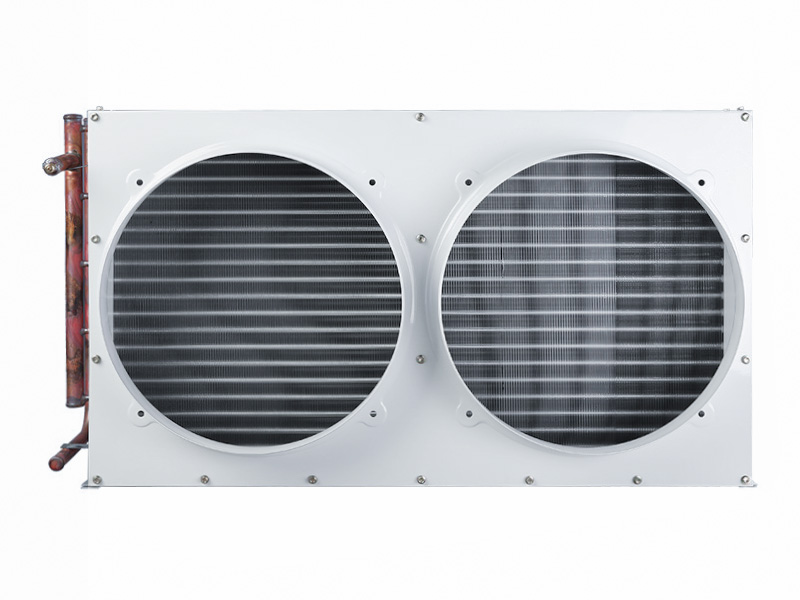
US projects
2023/03/08
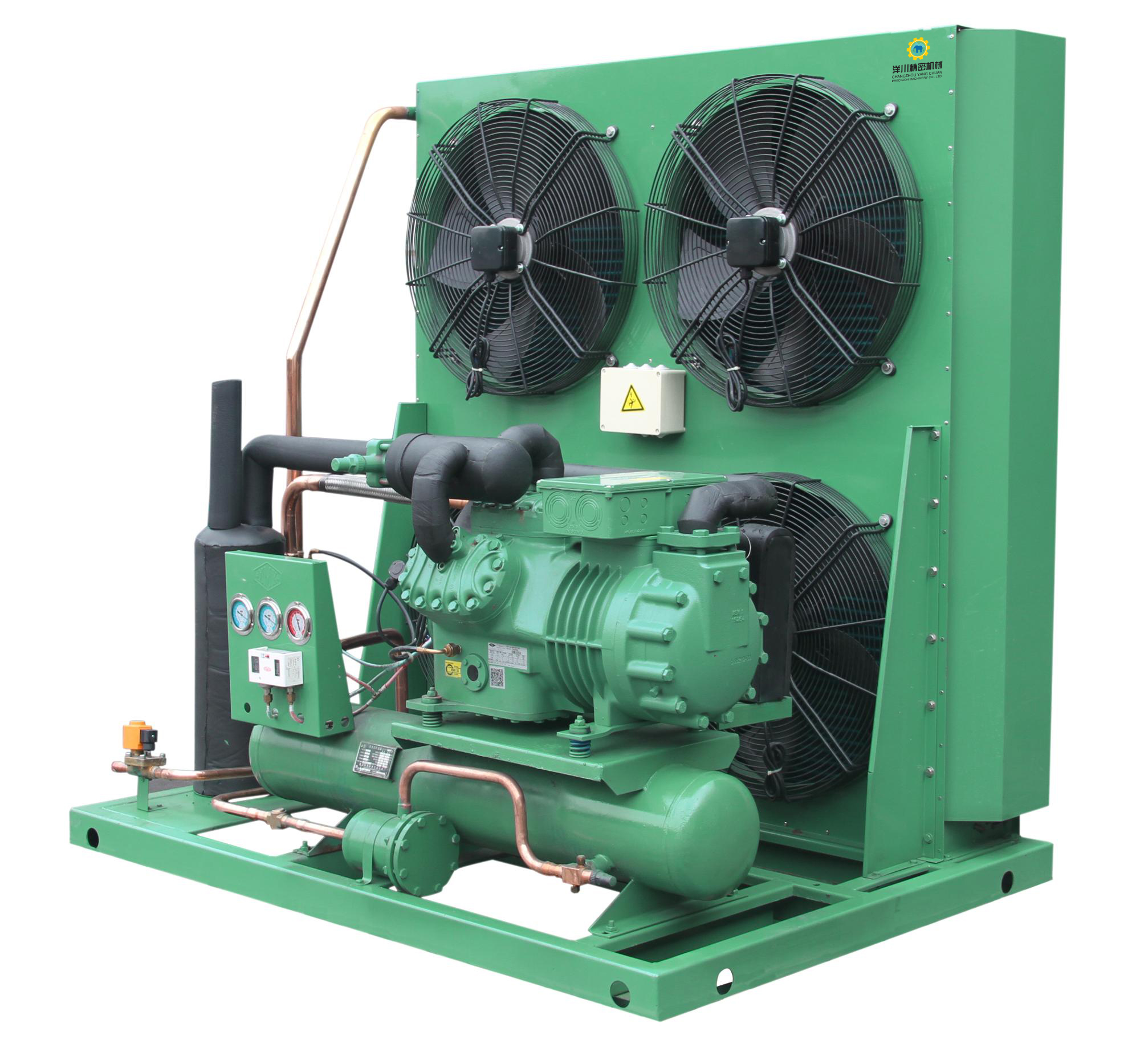
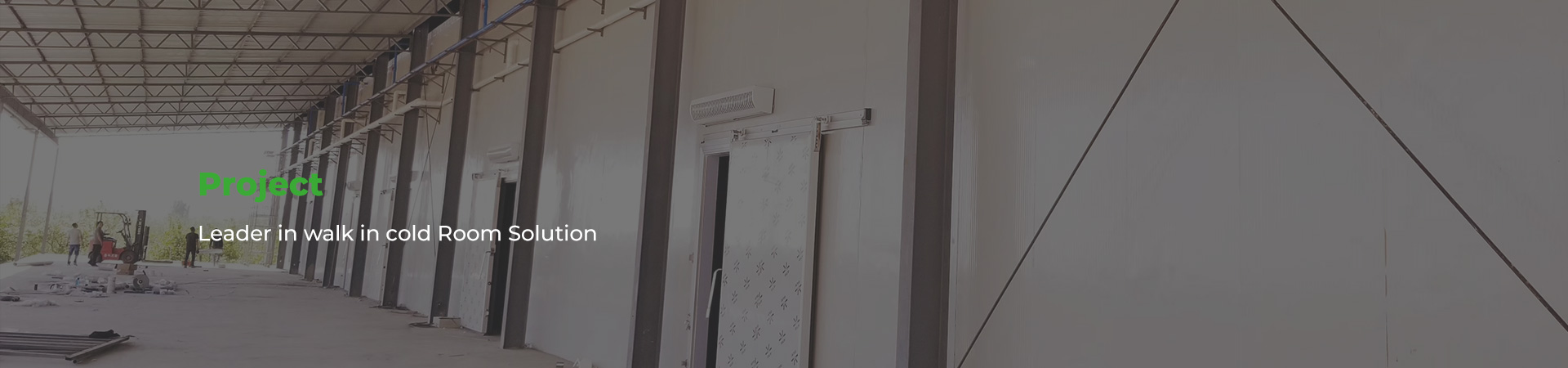
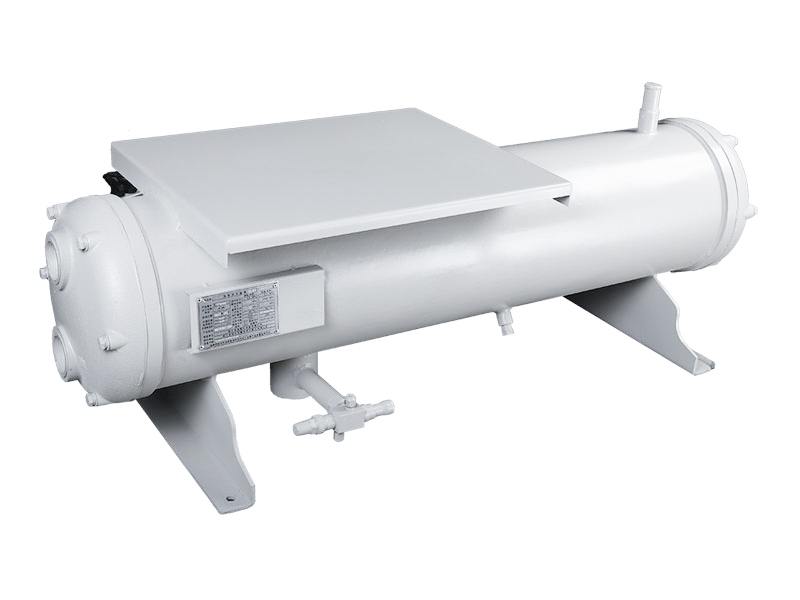
Yangchuan has won high praise from customers in more than 110 countries around the world. We are committed to developing solutions that best suit customers' needs and walk-in cold room, so as to improve customers’ profitability and achieve sustainable bus

- Prev: Japan project
- Next: Cold Room